Customs clearance is one of the most crucial steps in the import and export process.
Understanding the vital role of customs declaration and clearance, Trường Thành Logistics has continuously improved and perfected its services. As a result, we are committed to meeting the maximum needs of businesses, making a significant contribution to the success of every shipment.

Trường Thành Logistics provides customs declaration services for the following activities:
- Commercial import and export
- Import and export for processing
- Import and export for production
- On-the-spot import and export
- Temporary export for re-import, temporary import for re-export
- Capital contribution import and export (taxable and tax-exempt)
1. Customs Procedures for Imports
Below are the steps required for handling customs procedures for imports. However, there may be some differences in the process for specific types of goods or products.

Để nắm bắt chính xác, chi tiết các công việc cần làm, bạn có thể tìm hiểu trước một cách kỹ càng, liên hệ với cơ quan hải quan hoặc nhờ sự tư vấn của Trường Thành Logistics.
To get precise and detailed information on the necessary tasks, you can conduct thorough research beforehand, contact the customs authority, or seek advice from Trường Thành Logistics.
1.1. Preparation: Gather the following documents for customs declaration:
- Import permit (if the goods require a license for import)
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading
- Certificate of Origin (C/O)
- Fumigation Certificate and Phytosanitary Certificate (if applicable)
- Certificate of Analysis (C/A)
- Certificate of Quality (C/Q) (if applicable)
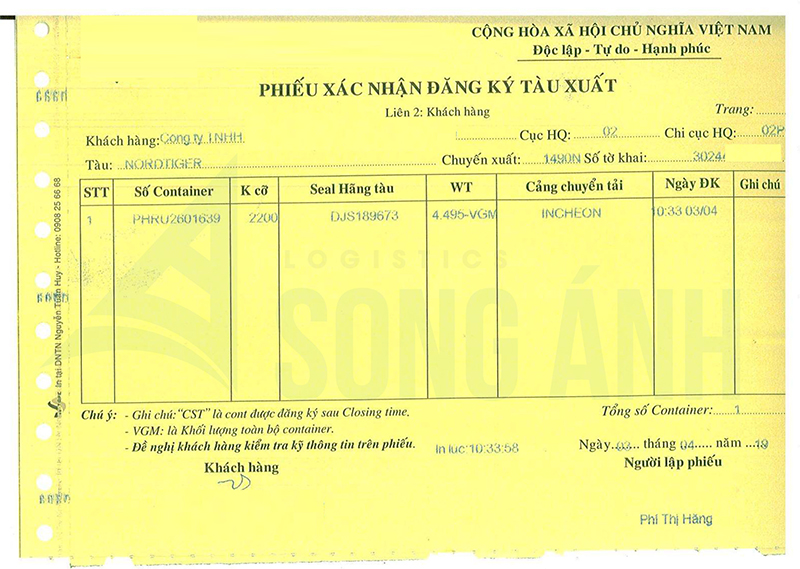
1.2. The Process
Step 1: Declare Import Information (IDA) The customs declarant uses the IDA operation to declare import information before registering the customs declaration form.
After all 133 fields on the IDA screen are filled, the declarant sends the data to the VNACCS system. The system automatically assigns a number, populates fields related to tax rates and corresponding names (for example: the name of the importing country corresponding to the country code, the name of the importing company corresponding to the enterprise code, etc.), and automatically calculates values related to customs value and taxes.
The system then sends a response back to the declarant on the declaration registration screen (IDC). Once the system assigns a number, the IDA import information form is saved on the VNACCS system.
Step 2: Register the Import Declaration Form (IDC) Upon receiving the IDC screen from the system, the customs declarant checks the declared information and the automatically populated and calculated data. If the information is confirmed to be accurate, it is sent to the system to register the declaration.
If, after checking, the declarant finds that the information is inaccurate and needs to be amended, they must use the IDB operation to recall the IDA import information screen, make the necessary corrections, and follow the same steps as above.
Step 3: Check Conditions for Declaration Registration Before allowing a declaration to be registered, the system automatically checks the list of enterprises ineligible for declaration registration (e.g., businesses with overdue debts over 90 days, those that are temporarily suspended, dissolved, or bankrupt).
If the enterprise is on the aforementioned list, the declaration cannot be registered, and the system will notify the customs declarant. If the conditions are met, the enterprise can proceed to the next steps.
Step 4: Channeling, Inspection, and Clearance Once the declaration is registered, the system automatically assigns it to one of three channels: Green, Yellow, or Red.
For declarations in the Green Channel:
- If the tax payable is zero: The system automatically grants customs clearance (expected to take 3 seconds) and issues an “Imported Goods Customs Clearance Decision” to the declarant.
- If the tax payable is not zero:
- If the tax is declared to be paid by a credit limit or via a guarantee (general or specific): The system automatically checks the declared information related to the limit or guarantee. If the amount is greater than or equal to the tax payable, the system will issue a “Document Noting Tax Payable” and an “Imported Goods Customs Clearance Decision” to the declarant. If the amount is less than the tax payable, the system will report an error.
- If tax is declared to be paid immediately (bank transfer, cash at the customs office, etc.): The system issues a “Document Noting Tax Payable” to the declarant. Once the customs declarant has paid the taxes, fees, and charges, and the VNACCS system has received the payment information, the system issues a “Goods Customs Clearance Decision.” At the end of the day, the VNACCS system compiles all cleared Green Channel declarations and transfers them to the VCIS system.
For declarations in the Yellow and Red Channels: The system transfers the data of Yellow and Red Channel declarations online from VNACCS to VCIS. After the customs authority performs checks and processes the declaration on the VCIS system screen, using CKO or CEA operations to complete or provide guidance, the customs declarant must take the following steps:
- Receive the system’s response regarding the channeling result, location, and type/level of physical inspection of the goods.
- Submit the paper documents for the customs authority to conduct a detailed review; prepare the goods for physical inspection.
- Fulfill all tax and fee obligations (if any).
Step 5: Amending and Supplementing Declarations During Clearance The system allows for amendments and supplements to the declaration from the time it is registered until the goods are cleared.
To perform an amendment or supplement during clearance, the customs declarant uses the IDD operation to recall the full import declaration information screen (IDA) for the first amendment, or the most recent amended import information (IDA01) for the second amendment or subsequent ones.
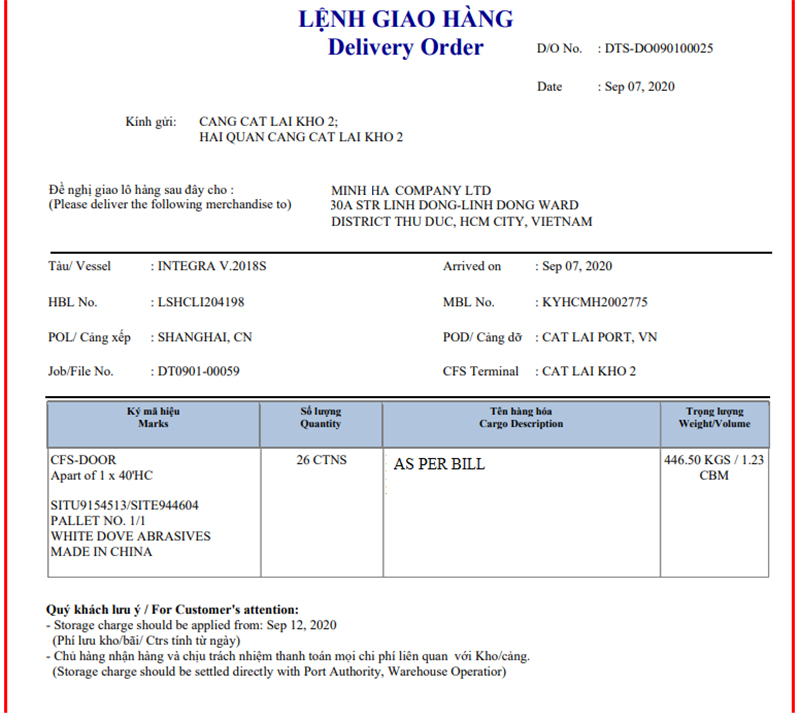
2. Customs Procedures for Exports
2.1. An Overview of Export Customs Procedures
The steps for export customs procedures are quite similar to those for imports. To proceed with customs formalities for exports, businesses need to follow the steps below.
2.2. The Process
Step 1: Declare Export Information (EDA) The customs declarant uses the EDA operation to declare export information before registering the export declaration form.
After all 109 fields on the EDA screen are filled, the declarant sends the data to the VNACCS system. The system automatically assigns a number, populates fields related to tax rates and corresponding names (for example: the name of the destination country corresponding to the country code, the name of the exporting company corresponding to the enterprise code, etc.), and automatically calculates values related to customs value and taxes.
The system then sends a response back to the declarant on the declaration registration screen (EDC). Once the system assigns a number, the EDA export information form is saved on the VNACCS system.
Step 2: Register the Export Declaration Form (EDC) Upon receiving the EDC screen from the system, the customs declarant checks the declared information and the automatically populated and calculated data. If the information is confirmed to be accurate, it is sent to the system to register the declaration.
If, after checking, the declarant finds that the information is inaccurate and needs to be amended, they must use the EDB operation to recall the EDA export information screen, make the necessary corrections, and follow the same steps as above.
Step 3: Check Conditions for Declaration Registration Before allowing a declaration to be registered, the system automatically checks the list of enterprises ineligible for declaration registration (e.g., businesses with overdue debts over 90 days, those that are temporarily suspended, dissolved, or bankrupt).
If the enterprise is on the aforementioned list, the declaration cannot be registered, and the system will notify the customs declarant.
Step 4: Channeling, Inspection, and Clearance Once the declaration is registered, the system automatically assigns it to one of three channels: Green, Yellow, or Red.
For declarations in the Green Channel:
- If the tax payable is zero: The system automatically grants customs clearance (expected to take 3 seconds) and issues a “Goods Customs Clearance Decision” to the declarant.
- If the tax payable is not zero:
- If the tax is declared to be paid by a credit limit or via a guarantee (general or specific): The system automatically checks the declared information related to the limit or guarantee. If the amount is greater than or equal to the tax payable, the system will issue a “Document Noting Tax Payable” and a “Goods Customs Clearance Decision” to the declarant. If the amount is less than the tax payable, the system will report an error.
- If tax is declared to be paid immediately (bank transfer, cash at the customs office, etc.): The system issues a “Document Noting Tax Payable” to the declarant. Once the customs declarant has paid the taxes and fees and the VNACCS system has received the payment information, the system issues a “Goods Customs Clearance Decision.” At the end of the day, the system compiles all cleared Green Channel declarations and transfers them to VCIS.
For declarations in the Yellow and Red Channels: The system transfers the data of Yellow and Red Channel declarations online from VNACCS to VCIS. The customs authority will then check and process the declaration on the VCIS system screen, using CKO or CEE operations to proceed or inform the declarant of the next steps. The customs declarant will then:
- Receive the system’s response regarding the channeling result, location, and type/level of physical inspection of the goods.
- Submit paper documents for the customs authority to conduct a detailed review; prepare the goods for physical inspection.
- Fulfill all tax and fee obligations (if any).
Step 5: Amending and Supplementing Declarations During Clearance Amending and supplementing the declaration can be done from the time it is registered until the goods are cleared. To perform this, the customs declarant uses the EDD operation to recall the export declaration information (EDA) for the first amendment, or the most recent amended export information (EDA01) for the second amendment or subsequent ones.
Thus, it’s clear that whether a business is handling customs procedures for import or export, they need a solid grasp of customs regulations.
If you have any questions or want to ensure your company’s documents are approved quickly and with minimal risk of deficiencies, contact Trường Thành Logistics today. You can also learn about our entrusted import and export services and how they can benefit your business.
With over 12 years of experience in logistics and customs clearance, our team at Trường Thành Logistics will help your business complete your customs documents simply and quickly.
Trường Thành Logistics – Professional & Dedicated
Hotline: +84 915 36 38 39
Head Office: 5th Floor, Tower A, Song Da Building, Pham Hung Street, Tu Liem Ward, Hanoi, Vietnam.
Email: sale@truongthanhjsc.com
info@truongthanhlogistics.com
Website: https://truongthanhlogistics.com
HAI PHONG BRANCH
Address: Room C103, TTC Building, 630 Le Thanh Tong Street, Hai An Ward, Hai Phong City, Vietnam.
DA NANG BRANCH
Address: 126 Chau Thi Vinh Te Street, Ngu Hanh Son Ward, Da Nang City, Vietnam.
HO CHI MINH CITY BRANCH
Address: Room 41, 4th Floor, Casanova Building, 85 Nguyen Son Street, Phu Thanh Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam











