D/O is an indispensable document in the process of importing and exporting goods by sea. A clear understanding of D/O and related regulations will help businesses effectively manage the process of receiving and delivering goods and minimizing risks.
The concept and role of D/O in import and export
D/O, short for “Delivery Order,” is an important document in the process of importing and exporting goods. D/O is issued by the shipping line or freight agent to instruct the port or warehouse to hand over the shipment to the consignee.
D/O plays an important role in the process of importing and exporting goods with the following main functions:
+ Certificate of ownership of goods: D/O confirms that the consignee has the right to receive the shipment from the port or warehouse.
+ Delivery instructions: D/O provides detailed instructions on the delivery of goods, including information about the recipient, location and time of receipt.
+ Management and control of goods: D/O helps manage and control the delivery process, ensuring that goods are delivered to the right person and at the right time.
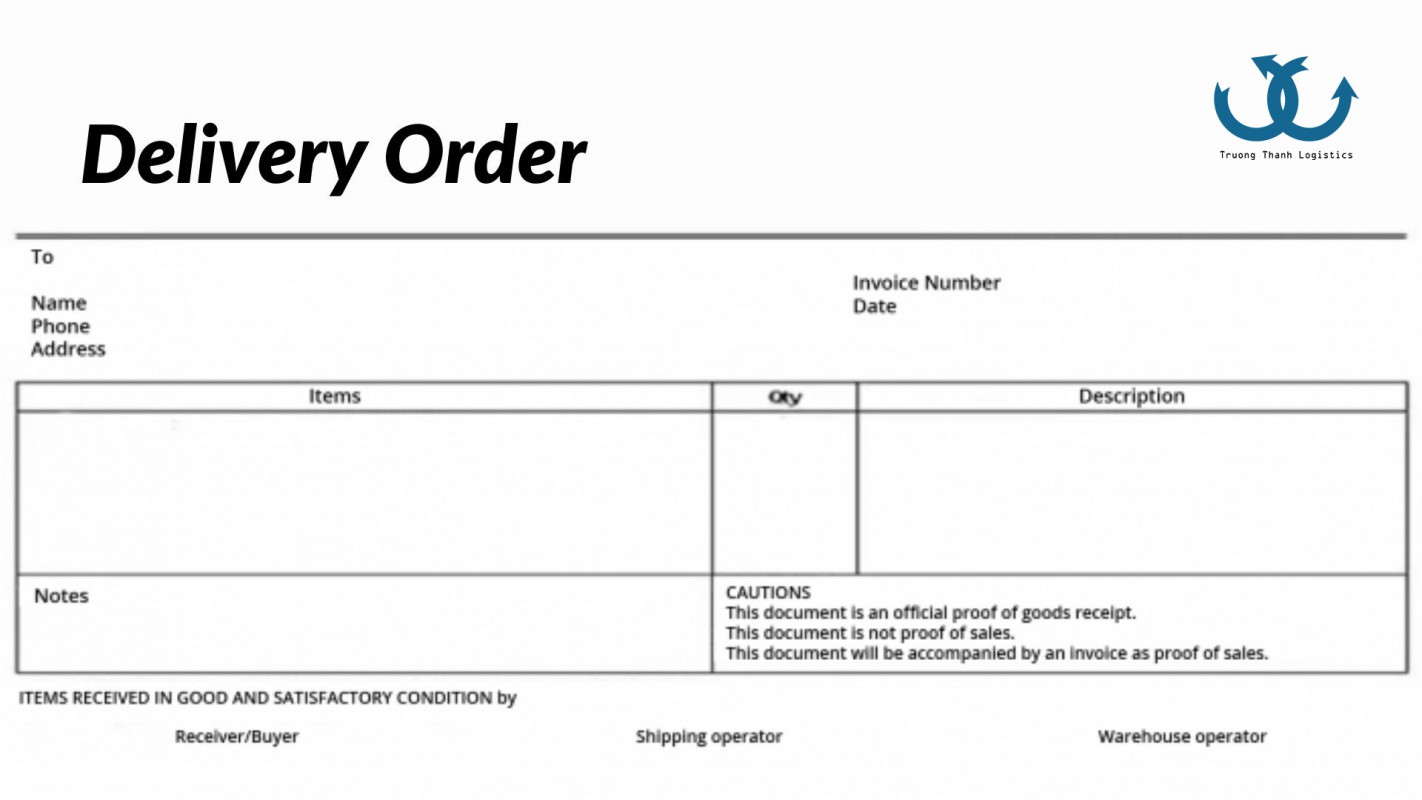
Common types of D/O
D/O is divided into many different types, each with its own characteristics and applications. Below are some of the most common types of D/O:
Forwarder’s D/O (D/O of freight forwarding company): Forwarder’s D/O is a type of D/O issued by a freight forwarding company (forwarder) on behalf of the shipping line. The forwarder is responsible for arranging the transportation of goods and managing related procedures.
Carrier’s D/O (D/O of shipping line): Carrier’s D/O is a type of D/O issued directly by the shipping line. The shipping line is responsible for transporting goods from the port of export to the port of import and providing D/O to the consignee.
House D/O (D/O of the shipping agent or logistics company): House D/O is a type of D/O issued by a shipping agent or logistics company, usually in cases where goods are transported in the form of consolidation.
Master D/O (Main D/O): Master D/O is a type of D/O issued by the shipping line or main carrier to the shipping agent or logistics company when transporting goods in the form of consolidation.
In addition to the above classification, D/O can be classified according to other criteria such as:
+ Original D/O (Original Bill of Lading): Is the only original document, with the highest legal value.
+ Electronic D/O (Electronic Bill of Lading – EDO): Is an electronic copy of the original D/O, stored and transmitted via an electronic system.
+ Beneficiary D/O (Order Bill of Lading): D/O only delivers goods to the person named on the document or the person authorized by this person.
+ Straight Bill of Lading: D/O delivers goods directly to the consignee named on the document, without transfer.
+ House Bill of Lading: Bill of lading issued by the multimodal carrier.
+ Through Bill of Lading: Multimodal bill of lading, used when goods are transported by many different modes.
Choosing the appropriate type of D/O depends on many factors such as:
+ Type of goods: High-value goods often require the use of original D/O.
+ Terms of transaction: The terms in the sales contract will determine the type of D/O used.
+ Relationship between shipper and consignee: If the two parties have a trusting relationship, a non-beneficiary D/O can be used
Important terms in D/O
+ Departure and destination: Specify where the goods are loaded onto the ship and where the goods will be delivered.
+ Name of goods: Detailed description of the type of goods, quantity, weight.
+ Delivery terms: Specify delivery terms such as FOB, CFR, CIF, etc.
+ Freight: Specify the amount of freight that the shipper must pay.

Other frequently asked questions about D/O
+ How many times can a D/O be transferred? A D/O can be transferred many times until the goods are delivered to the final recipient.
+ How long is a D/O legally valid? The legal validity of a D/O usually lasts until the goods are delivered and customs procedures are completed.
+ Difference between D/O and commercial invoice: D/O is a transport document, while commercial invoice is a document proving the sale of goods.
How to handle when D/O is lost or damaged
+ Notify the shipping line: As soon as the D/O is discovered to be lost or damaged, the owner must immediately notify the shipping line to request a re-issue of D/O.
+ Marine insurance: If there is marine insurance, the owner can claim compensation for damages.
+ Customs procedures: The loss of D/O can cause difficulties in customs procedures, so it is necessary to contact the customs authority for instructions.
The above is important information about D/O. For assistance with import and export information, international freight, sea transport or import entrustment, please contact Truong Thanh Logistics at the address:
Truong Thanh Logistics – Dedication, Prestige
Hotline: 0915 36 38 39
Headquarter: 26th Floor, Tower A, Song Da Building, Pham Hung, Nam Tu Liem, Hanoi.
Email: sale@truongthanhjsc.com
info@truongthanhlogistics.com
Website: www.truongthanhlogistics.com
Hai Phong Branch
Address: R.A11, TTC Building, 630 Le Thanh Tong, Hai An, Hai Phong
Da Nang Branch
Address: 27 Nguyen Ba Lan, My An Ward, Ngu Hanh Son District, Da Nang.
HCMC Branch
Address: Room 41, 4th floor, Casanova building, 85 Nguyen Son street, Phu Thanh ward, Tan Phu district, Ho Chi Minh City











